Nittobo Group strives to contribute to the realization of an enriched society,
serves as a valued corporate group in society, and commits to the creation of comfortable life.
Glass cloth for electronic materials
Glass cloth for printed wiringboards

One of the greatest uses of glass cloth is as electric insulating base materials that make the most of such glass fiber properties as electric insulation, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.
Combined with materials, such as epoxy resin and polyimide resin, glass cloth is used for the manufacture of printed wiringboards of electronic equipment (such as computers, communications devices, and switchboards). Higher value can be added to printed wiringboards by applying glass cloth processing technology (fiber opening technology), a field dominated by Nittobo.
printed wiringboard model (cross section)
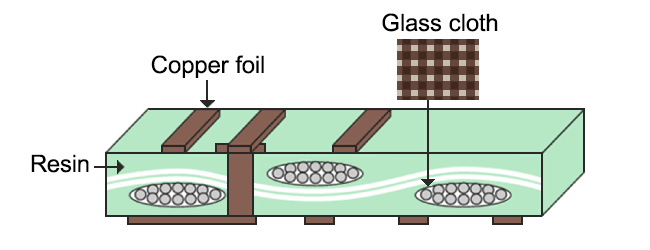
Note) Glass cloth is not used for all printed wiringboards.
Glass cloth specifications
| IPC specifications (excerpts) | Thickness (mm) | Weight (g/m²) | Density (/25mm) | Manner of weaving | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp | Weft | ||||
| 106 | 0.035 | 25 | 56 | 56 | Plain weave |
| 1080 | 0.055 | 47 | 60 | 46 | Plain weave |
| 3313 | 0.075 | 83 | 60 | 62 | Plain weave |
| 2116 | 0.095 | 104 | 60 | 58 | Plain weave |
| 1504 | 0.125 | 148 | 60 | 50 | Plain weave |
| 1501 | 0.140 | 165 | 46 | 45 | Plain weave |
| 7628 | 0.180 | 209 | 44 | 32 | Plain weave |
High performance glass cloth
With the remarkable development of digital technology, electronic equipment typified by PCs and smartphones has become increasingly lightweight, thin, small, and functional, and manufacturers are strongly urged to enhance the characteristics of glass cloth.
Based on the development of glass composition and textile technology as well as textile processing technology, Nittobo offers glass cloth products, making the most of its strengths as an integrated manufacturer.
Low-dielectric-property glass cloth (NE glass)
As computers, mobile terminals, and communications infrastructure have evolved into increasingly high-speed, high-frequency systems, manufacturers of printed wiringboards have been required to use low-dielectric-property materials to reduce transmission loss. To that end, Nittobo has achieved low dielectric constant and low dielectric dissipation factor using NE-glass yarn that it has developed independently rather than conventional E glass.
| Dielectric constant (1GHz) | Dielectric dissipation factor (1GHz) | |
|---|---|---|
| E glass | 6.8 | 0.0035 |
| NE glass | 4.8 | 0.0015 |
- * All data listed above are examples of actually measured values and not standard ones.
Low-CTE glass cloth (T glass)
Excellent dimensional stability and increased rigidity can be achieved using T-glass yarn, which is characterized by its low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and high tensile elasticity.
| Thermal expansion coefficient (×10-6/℃) | Tensile elasticity modulus (GPa) | |
|---|---|---|
| E glass | 5.6 | 75 |
| T glass | 2.8 | 86 |
- * All data listed above are examples of actually measured values and not standard ones.
Ultra-thin glass cloth
Thinner glass cloth is desired for materials to meet the requirements of printed wiringboards as such materials are used at high densities and have become increasingly lightweight, thin, and small. Not only is Nittobo's ultra-thin glass cloth exceptionally thin, it excels in the ability to make very small holes in both laser and drill processing as well. Furthermore, this material is excellent in terms of lamination characteristics, such as dimensional stability and surface smoothness.
| IPC specifications (excerpts) |
Thickness (mm) |
Weight (g/m²) |
Density (/25mm) | Manner of weaving |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp | Weft | ||||
| 1037 | 0.025 | 24 | 69 | 72 | Plain weave |
| 1027 | 0.020 | 19 | 74 | 74 | Plain weave |
| 1017 | 0.015 | 13 | 95 | 95 | Plain weave |
| 1010 | 0.013 | 10 | 95 | 95 | Plain weave |
- * All data listed above are examples of actually measured values and not standard ones.
- Business introduction
- Glass Fiber
- What is glass fiber?
- Special materials
- Composite materials
- Yarn
- High-performance glass cloth
- Industrial materials
Interior furnishings market
Market for exterior furnishings
Construction market
Lifestyle, sports, and leisure markets
Media market
Automobile and aircraft markets
Heat resistance and heat insulation markets
Civil engineering market
Market for industrial base materials
- Medical
- Textile
